Authors:
Niedzwiedzki, D. M., Bar-Zvi, S., Blankenship, R. E., & Adir, N. (2019)
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 1860(4), 286-296.
Abstract:
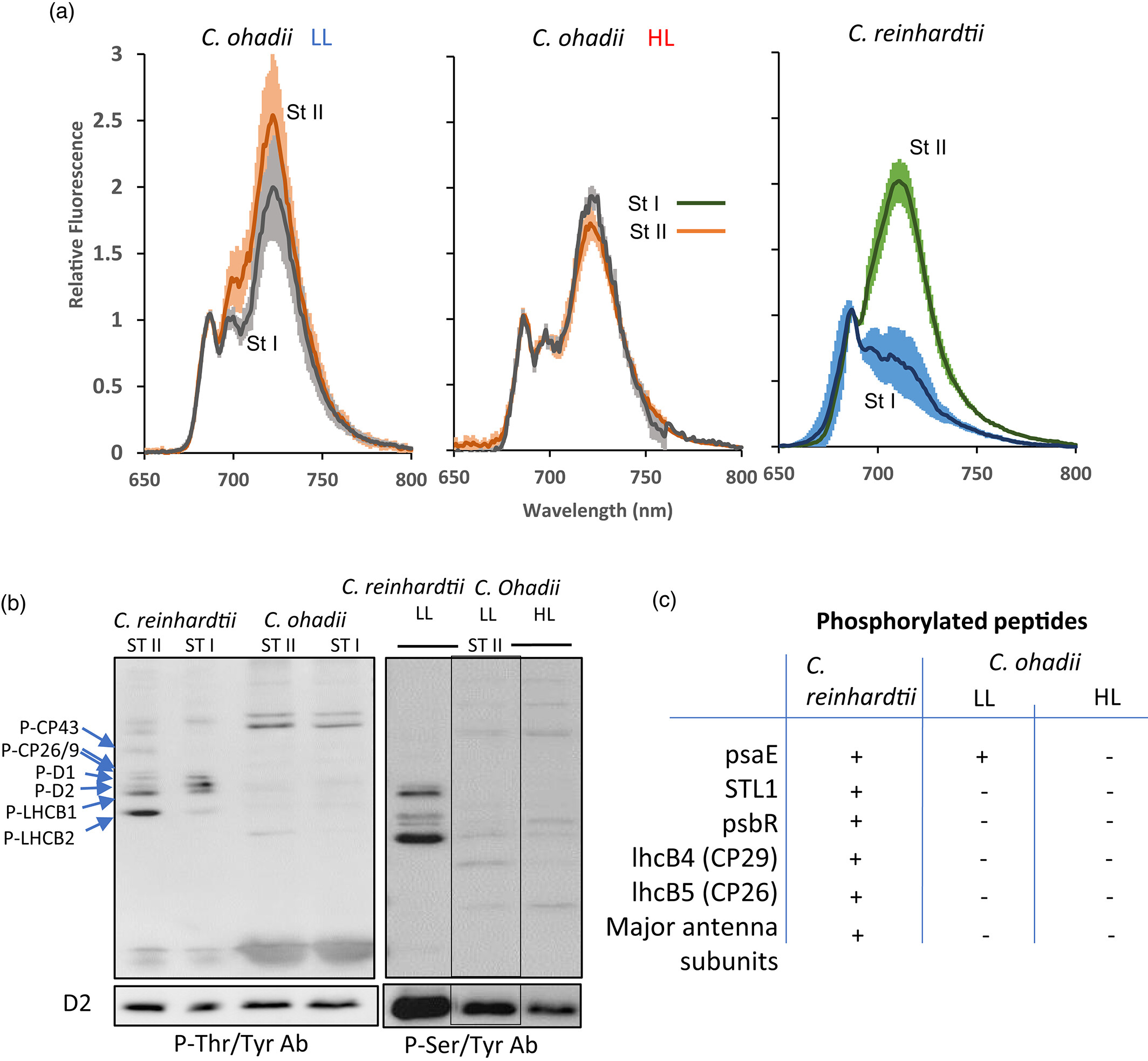
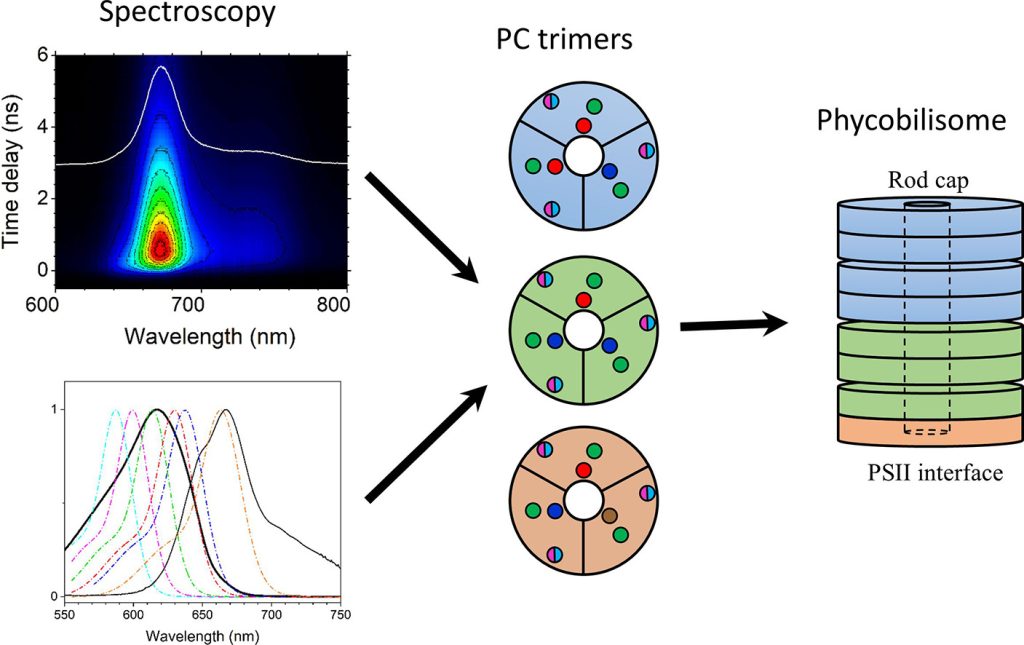
In this study, we use ultrafast time-resolved absorption and fluorescence spectroscopies to examine A. marina phycobilisomes isolated from cells grown under light of different intensities and spectral regimes. Investigations were performed at room temperature and at 77 K. The study demonstrates that if complexes are stabilized by high phosphate (900 mM) buffer, there are no differences between them in temporal and spectral properties of fluorescence. However, when the complexes are allowed to disassemble into trimers in low phosphate (50 mM) buffer, differences are clearly observed. The fluorescence properties of intact or disassembled phycobilisomes from cells grown in low intensity white light are unresponsive to variation in phosphate concentration. This antenna complex was further studied in detail with application of femtosecond time-resolved absorption at room temperature. Combined spectroscopic and kinetic analysis of time-resolved fluorescence and absorption data of this antenna allowed us to identify spectrally different forms of phycocyanobilins and to propose a simplified model of how they could be distributed within the phycobilisome structure.
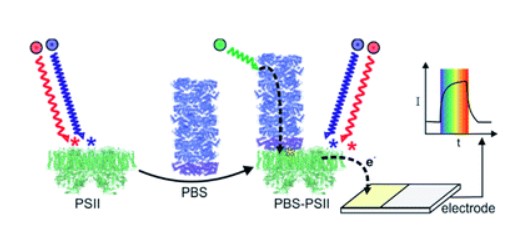
Model of the Phycobilisome (blue and cyan discs). Multiple complexes are situated in between two photosynthetic membranes close to Photosystem II (green) and Photosystem I (yellow)
Artwork by Itai Goldschmid
Highlights
- A. marina phycobilisomes grown in light of different intensities and spectral ranges studied with time-resolved spectroscopy
- Fluorescence properties of phycobilisome from cells grown in low intensity white light unresponsive to low phosphate buffer
- Spectroscopic and kinetic analysis of this phycobilisome allows identify spectrally different forms of phycocyanobilins
- A minimal model of how they are distributed within the phycobilisome structure proposed