Authors:
A. Shahar, M. Melamed-Frank, Y. Kashi, L. Shimon and N. Adir.
Journal of Molecular Biology, 412, 192-203 (2011)
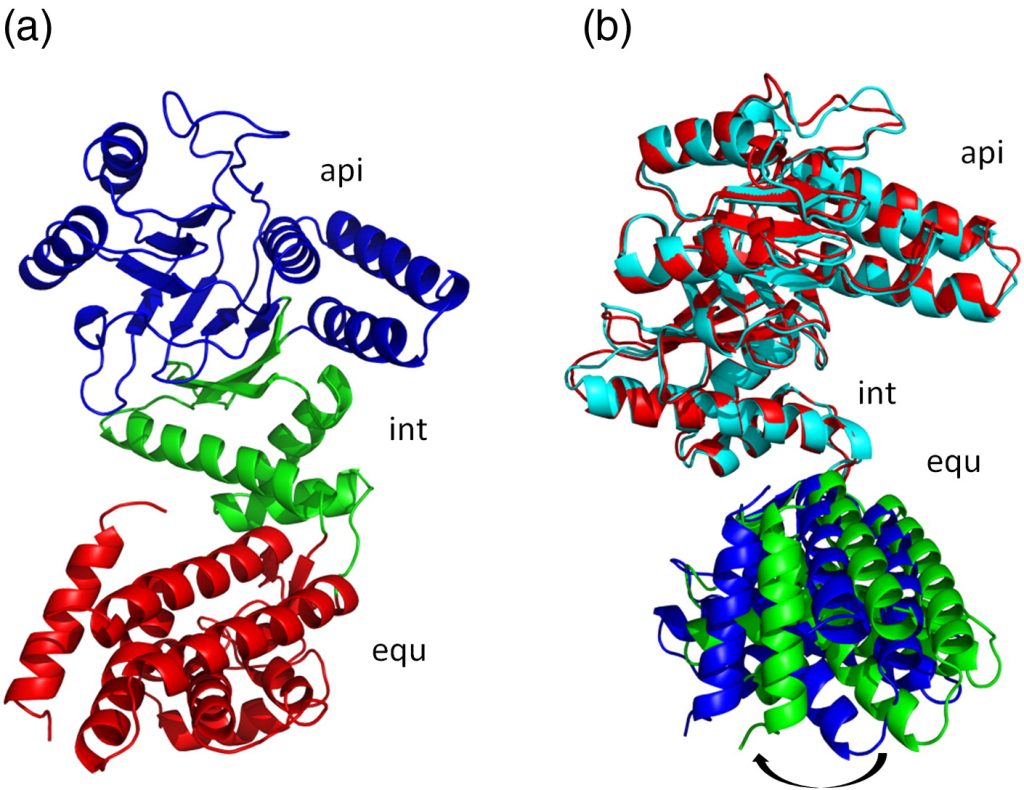
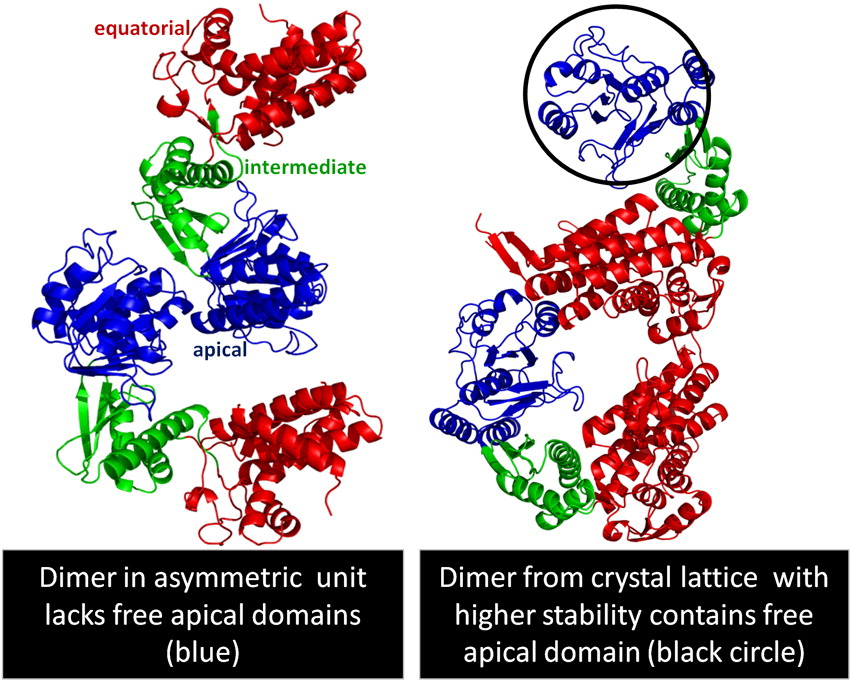
Fig. 1. Structure of Cpn60.2. (a) Structure of the Cpn60.2 monomer. Equatorial (equ), intermediate (int), and apical (api) domains are depicted in red, green, and blue cartoons, respectively. (b) Superposition of two Cpn60.2 monomers in the AU dimer. Subunits A (red and blue cartoons) and B (cyan and green cartoons) were superposed for all Cα atoms in the int and api domains to reveal the change in the equ domain position by about 5°. All molecular graphics were made using PyMOL.40
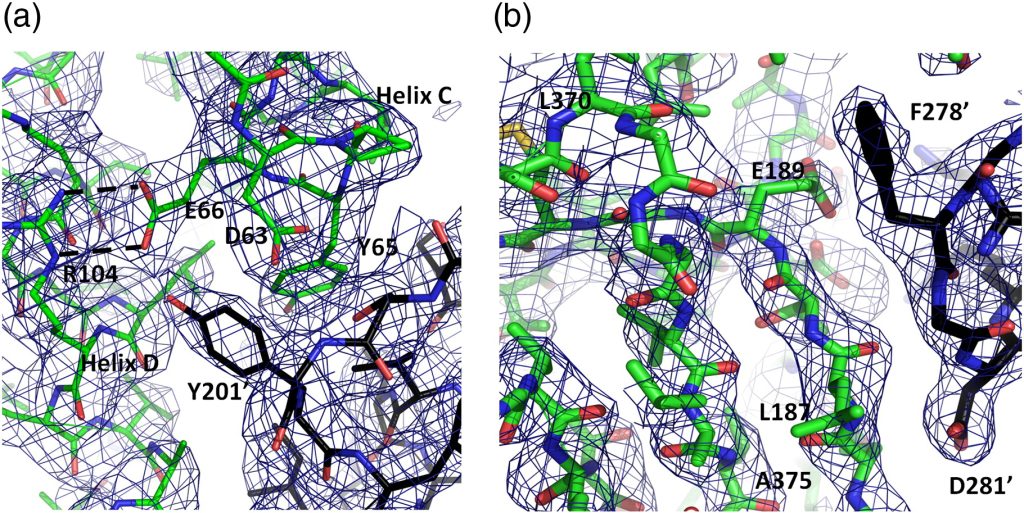
Fig. 2. Quality of the Cpn60.2 structure. A composite omit electron density map calculated with CNS36 was contoured (1σ) over the Cpn60.2 structure. (a) The N-terminus of the B subunit showing interactions between helices C and D (green sticks) and the apical domain of a symmetry-related molecule (black sticks). Blue and red sticks represent nitrogen and oxygen atoms, respectively. (b) The intermediate domain of monomer A and its interaction with a symmetry-related apical domain. Colors as in (a). Residues noted from the symmetry-related molecules are denoted by an apostrophe.